 |
Image credit – nature Scientific Reports |
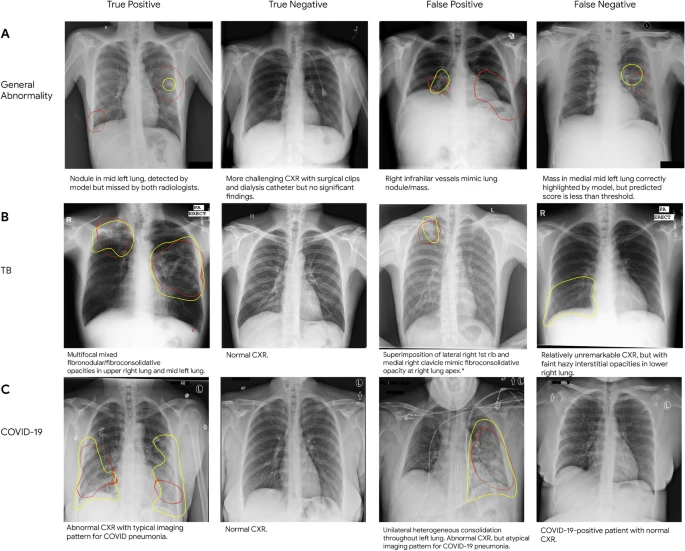
Once trained, the researchers tested the AI algorithms on new patients and unseen diseases using datasets from the Apollo Hospital in India and publicly available chest x-rays. In a simulated workflow the time it took normally to flag abnormal cases for radiological review was reduced by 7%-28%, allowing for prompt patient workups and management.
“These results represent an important step towards evaluating whether AI can be safely used to flag cases in a general setting where previously unseen abnormalities exist,” the team wrote in their paper, which was published in the nature journal Scientific Reports.
The researchers concluded that when compared to radiologists reading the same datasets, the AI algorithm outperformed the radiologists in distinguishing certain types of abnormalities, suggesting that as a prioritization tool the algorithm could be particularly useful in emergency medicine settings.
The researchers released their datasets to the public in an effort to provide a useful resource to facilitate the continued development of clinically useful AI models for chest x-ray interpretation.
Source: nature Scientific Reports

No comments:
Post a Comment